Dysmenorrhoe Problem
Primary Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea refers to painful cramping pain accompanying menstruation. It occurs around the time that menstruation begins and the symptoms typically last less than three days and the pain is usually in the pelvis or lower abdomen. Other symptoms may include back pain, diarrhea and nausea. Dysmenorrhea occurs less often in those who exercise regularly. Dysmenorrhea is the most common menstrual disorder in females of reproductive age. Usually the pain of dysmenorrhea improves with age or following having a child.
Just because the problem is quite common, females tend to think that it is normal to have painful menses. The fact is that it is not normal. Menstruation is a physiological process. There is no need for it be painful. In case pain occurs during periods, it needs to be treated.
Types:
Primary dysmenorrhea refers to one that is not associated with any identifiable pelvic pathology. It affects more than 50% of post pubescent women in the age groups of 18 to 25 years.
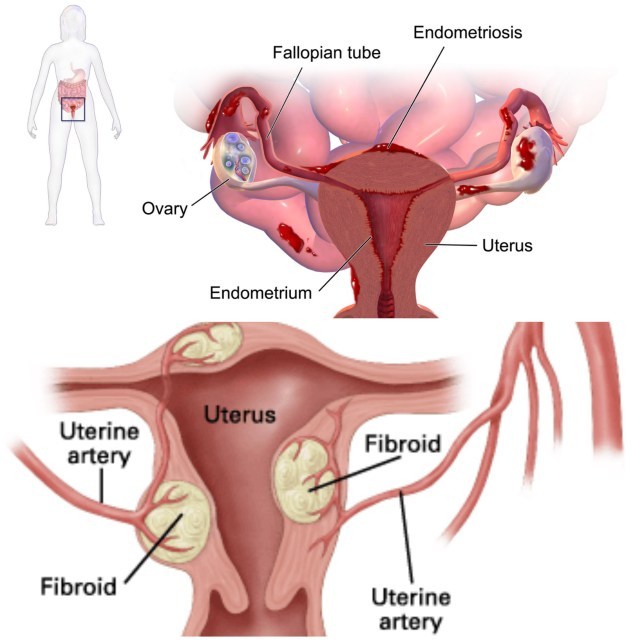
Secondary dysmenorrhea refers to the one associated with presence of organic pelvic pathology i.e. fibroids, adenomyosis, PID, endometriosis etc.
Varities:
Spasmodic dysmenorrhea is the most common variant of dysmenorrhea and manifest as cramping pains, generally most pronounced on the first and second day of menstruation.
Congestive dysmenorrhea manifest as increasing pelvic discomfort and pelvic pain a few days before the commencement of menses, this variety is commonly seen in pelvic inflammatory disease or pelvic endometriosis.
Membranous dysmenorrhea is a special group in which the endometrium is shed as a cast at the time of menstruation. The passage of the cast is accompanied by painful uterine cramps.
Clinical Features:
The main symptom of dysmenorrhea is pain concentrated in the lower abdomen or pelvis. It is also commonly felt in the right or left side of abdomen. It may radiate to thighS and lower back.
Symptoms often co-occurring with menstrual pain include nausea & vomiting, diarrhea or constipation, headache, dizziness, disorientation, hypersensitivity to sound, light, smell or touch, fainting and fatigue.
Symptoms of dysmenorrhea often begin immediately after ovulation and can last until the end of menstruation. This is because dysmenorrhea is often associated with changes in hormone level in the body that occur with ovulation. The use of certain types of birth control pills can prevent the symptoms of dysmenorrhea because they stop ovulation from occurring.
